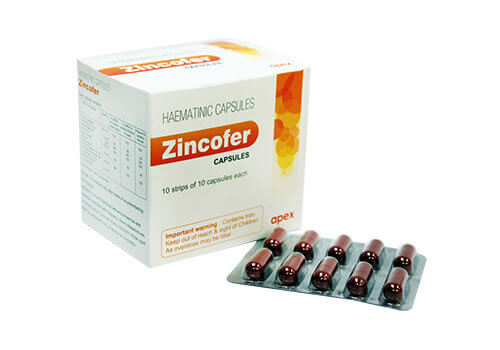
Zincofer capsules is the first haematinic offering zinc with iron and other important haemopoietic factors. Zincofer initiates DNA, RNA synthesis and ensures proper foetus formation. Zincofer prevent foetus malformations due to zinc deficiency in pregnancy. Zincofer corrects symptoms like perverted taste, loss of appetite and mental depression often observed during pregnancy. Zincofer corrects anaemia.
There is evidence that a daily dose of 100mg of elemental iron in the ferrous form is adequate to prevent development of iron deficiency in expectant mothers. If a mild iron deficiency is present when Zincofer administration is started, this will be corrected by increased absorption of iron. The daily folate requirement rises steeply during the final trimester of pregnancy, and evidence of maternal depletion may be found. To ensure normal tissue folate levels in the mother after delivery a daily supplement of about 300 micrograms is required during the second and third trimester of pregnancy. This does not obscure the blood picture of addisonian pernicious anaemia.
How haematinic capsules zincofer work:
Iron is absorbed chiefly in the duodenum and jejunum, absorption being aided by the acid secretion of the stomach and being more readily effected when the iron is in the ferrous state.
Folic acid is absorbed mainly from the proximal part of the small intestine. Folate polyglutamates are considered to be de-conjugated to monoglutamates during absorption. Folic acid rapidly appears in the blood, where it is extensively bound to plasma proteins. The amounts of folic acid absorbed from normal diets are rapidly distributed in body tissues and about 4 to 5 micrograms is excreted in the urine daily. When larger amounts are absorbed, a high proportion is metabolised in the liver to other active forms of folate and a proportion is stored as reduced and methylated folate. Larger amounts of folate are rapidly excreted in the urine.
Zincofer Capsule use for :
Zincofer is indicated in Iron deficiency anaemia, nutritional deficiency anaemia and anaemia associated with pregnancy, worm infestation etc.
There is evidence that a daily intake of 100mg of elemental iron in the ferrous form is adequate to prevent development of iron deficiency in expectant mothers. If a mild iron deficiency is present when Zincofer Capsules administration is started, this will be corrected by increased absorption of iron.
The daily folate requirement rises steeply during the final trimester of pregnancy, and evidence of maternal depletion may be found. To ensure normal tissue folate levels in the mother after delivery a daily supplement of about 300 micrograms is required during the second and third trimester of pregnancy. This does not obscure the blood picture of addisonian pernicious anaemia. Zincofer Capsules are indicated during the second and third trimester of pregnancy for prophylaxis against iron deficiency and megaloblastic anaemia of pregnancy. Pregaday Tablets are not intended as a treatment for established megaloblastic anaemia.
How to take
One capsule a day after meals or as prescribed by the Physician.
Adults: It is usual to begin therapy with Zincofer Capsules about the thirteenth week of pregnancy (see Precautions) either as routine prophylaxis or selectively if the haemoglobin concentration is less than 11g/100 ml (less than 75% normal).
One Capsule should be taken daily by mouth.
Children: Not applicable.
Route of administration: Oral route.













Reviews
There are no reviews yet.